Introduction
Wire mesh is an essential material used in a wide range of applications, from fencing and window screens to industrial sieves and animal enclosures. In this article, we will explore the common wire mesh gauge sizes and their uses, so you can choose the right gauge for your project.
In addition to gauge, there are other important factors to consider when selecting wire mesh, such as mesh count and pitch. We will delve deeper into these factors and provide examples of common applications for each gauge size.
1. What is wire mesh gauge
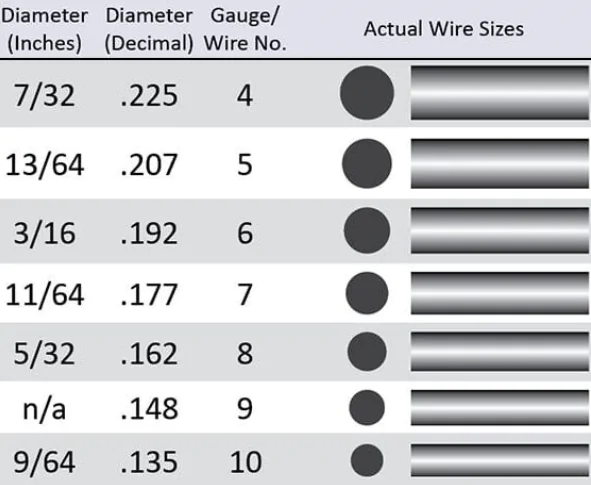
Wire mesh gauge refers to the thickness or diameter of the wire used to make a wire mesh. The gauge measurement system for wire mesh is based on a standardized numbering system, where smaller numbers represent thicker wires, and larger numbers represent thinner wires.
The gauge measurement system is used to provide a standard reference for wire mesh thickness and is based on the number of wire strands per inch. The wire strands are counted by placing a mesh sample under a microscope and counting the number of wires in one inch of the mesh.
The gauge number is determined by taking the number of wire strands per inch and subtracting it from the total number of strands in the mesh. For example, a 6-gauge wire mesh has six strands per inch and a 10-gauge wire mesh has ten strands per inch. The higher the gauge number, the thinner the wire.
Wire mesh gauges can range from as thin as 0.002 inches to as thick as 0.500 inches, depending on the application. Thicker gauges are used for heavy-duty applications, such as industrial sieves or security fencing, while thinner gauges are used for applications such as window screens or bird cages.
Wire mesh gauges are important to consider when selecting wire mesh for a specific application. The thickness of the wire can affect the strength, durability, and overall performance of the wire mesh. It is essential to select the appropriate gauge wire mesh for a specific application to ensure that it can withstand the required stress and perform its intended function.
2. Common wire mesh gauge sizes and their uses
The gauge of wire mesh is an essential consideration when selecting wire mesh for a specific application. It determines the thickness and strength of the wire and can impact the overall performance and durability of the wire mesh. Depending on the intended use, wire mesh is available in a wide range of gauges, with 10 gauge being the thickest and 16 gauge being the thinnest.
10 gauge wire mesh
The 10 gauge wire mesh is relatively thick and heavy-duty. It is commonly used in applications that require high strength and durability, such as industrial sieves, security fencing, and machine guards. 10 gauge wire mesh is also commonly used in animal enclosures, such as zoos and pet stores. It is often used as a barrier for large animals like lions and tigers, as well as for smaller animals like rodents and birds.
12 gauge wire mesh
The 12 gauge wire mesh is slightly thinner than the 10 gauge wire mesh, but still heavy-duty. It is commonly used in applications that require strength and durability, such as industrial shelving, machine guards, and fencing. 12 gauge wire mesh is also used in animal enclosures, such as aviaries and rodent cages. It is often used as a barrier for animals like parrots, canaries, and guinea pigs.
14 gauge wire mesh
14 gauge wire mesh is a medium-duty wire mesh that is commonly used in a variety of applications, including fencing, window screens, and ventilation systems. It is also used in the construction of outdoor furniture, such as patio chairs and tables. 14 gauge wire mesh is commonly used in garden and agricultural applications, such as plant supports and tree guards.
16 gauge wire mesh
16 gauge wire mesh is a lightweight wire mesh that is commonly used in applications that require flexibility and ease of installation, such as decorative wire mesh, window screens, and insect screens. It is also commonly used in arts and crafts applications, such as sculpture and jewelry making. 16 gauge wire mesh is often used in automotive applications, such as grill covers and air filters.
3. Other terms for wire mesh

Mesh count and pitch are two other terms related to wire mesh that are important to understand when selecting wire mesh for a specific application.
Mesh count
Mesh count refers to the number of wire strands per inch of wire mesh. For example, a wire mesh with a mesh count of 10 has 10 wire strands per inch in both the horizontal and vertical directions. Mesh count is an essential factor to consider when selecting wire mesh because it determines the size of the openings in the mesh.
The smaller the mesh count, the smaller the openings in the mesh, and vice versa. Mesh count can impact the mesh’s ability to filter or screen particles or objects of a certain size. A higher mesh count typically provides better filtration or screening capabilities.
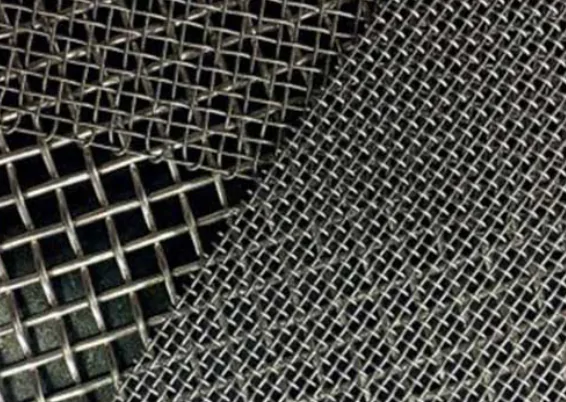

Pitch
Pitch is the distance between the centers of adjacent wires in the mesh. It is sometimes referred to as center-to-center spacing. Pitch is typically measured in inches or millimeters. Pitch is an essential factor to consider when selecting wire mesh because it determines the size of the openings in the mesh.
The larger the pitch, the larger the openings in the mesh, and vice versa. Pitch can impact the mesh’s ability to filter or screen particles or objects of a certain size. In some cases, the pitch can be adjusted to customize the wire mesh for a specific application.
Mesh count and pitch are important terms to understand when selecting wire mesh for a specific application. Mesh count determines the number of wire strands per inch of wire mesh and impacts the size of the openings in the mesh.
Pitch refers to the distance between the centers of adjacent wires in the mesh and also impacts the size of the openings in the mesh. Both mesh count and pitch can impact the mesh’s ability to filter or screen particles or objects of a certain size, and they may be adjusted to customize the wire mesh for a specific application.
Conclusion
Understanding the common wire mesh gauge sizes and their uses is crucial for anyone working with wire mesh. Whether you are building a fence or constructing an industrial sieve, selecting the right gauge will ensure the durability and effectiveness of your project.


